How to Find the Memory Address of a Symbol in an ELF File
A quick and useful tip for locating symbol memory addresses in ELF files using arm-none-eabi-nm combined with grep—perfect for embedded debugging scenarios like setting up SEGGER RTT or inspecting linker placements and runtime symbols.
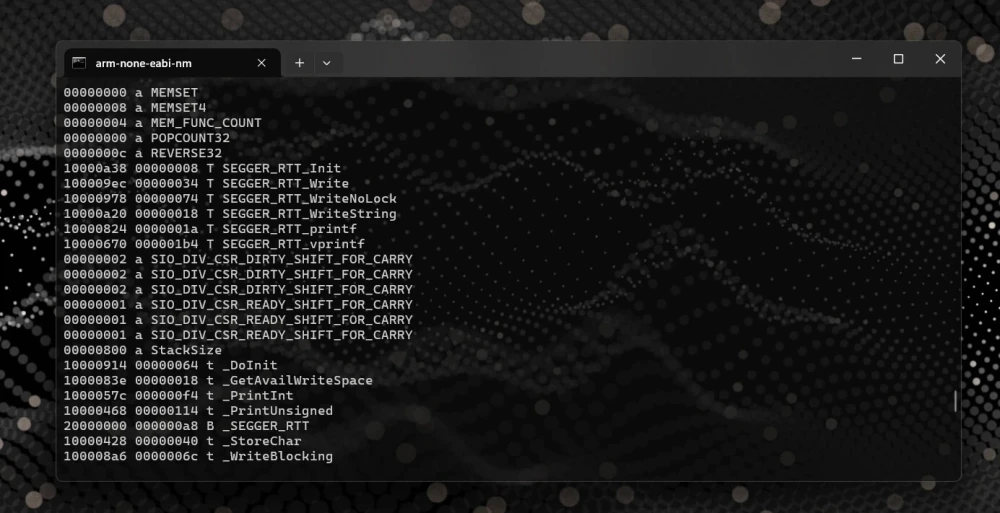
Here’s a handy tip that came up during some work with SEGGER RTT (Real Time Transfer).
When initializing an RTT session, you need to provide the memory address of the RTT static control block variable. While it’s possible to dig through your generated .map file, there's a faster way:
arm-none-eabi-nm blink.elf | grep _SEGGER_RTT
20000000 B _SEGGER_RTTBy piping the output of arm-none-eabi-nm (which lists all symbols in your .elf file) to grep, you can quickly isolate and retrieve the memory address of your desired symbol.
Note: For Windows users, grep is typically a Linux command. However, you can easily use this trick with tools like WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux), Cmder, or Git Bash.
arm-none-eabi-nm firmware.elf | grep foo
1000033c T fooThis technique isn't limited to variable addresses, it's equally useful for finding function or constant data addresses. Variable symbols are typically stored in volatile RAM, while function code and constant data usually reside in non-volatile ROM or Flash memory, reflecting their runtime mutability or immutability.
Getting Started with OpenOCD: A Beginner’s Guide for Embedded Developers
A beginner-friendly guide to installing, configuring, and using OpenOCD for flashing and debugging microcontrollers.

Cross-Compiling OpenOCD: A Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Learn how to build OpenOCD binaries on Ubuntu 22.04 for both the ARM64 and AMD64 target architectures. A great way to share a consistent OpenOCD build across your Debian systems

Advanced RTT in Embedded Rust: A Guide to Multi-Channel Logging and Binary Streaming (Part 2)
Stream RP2040 sensor data over RTT and decode logs in real time. Use Python to visualize binary temperature readings and turn raw bytes into insights.
Whether you're building something new, fixing stability issues, or automating what slows your team down — we can help.

